1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("I", "love", "you", "too"));
for(String str : list){
if(str.length()>3)
System.out.println(str);
}
list.forEach(str->System.out.println(str));
list.stream().filter(str->str.length()>3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
|
用stream的filter来替代if/else业务逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(....){
//...........
}else{
//.......
}
}
list.stream().filter().limit(10).foreach();
|
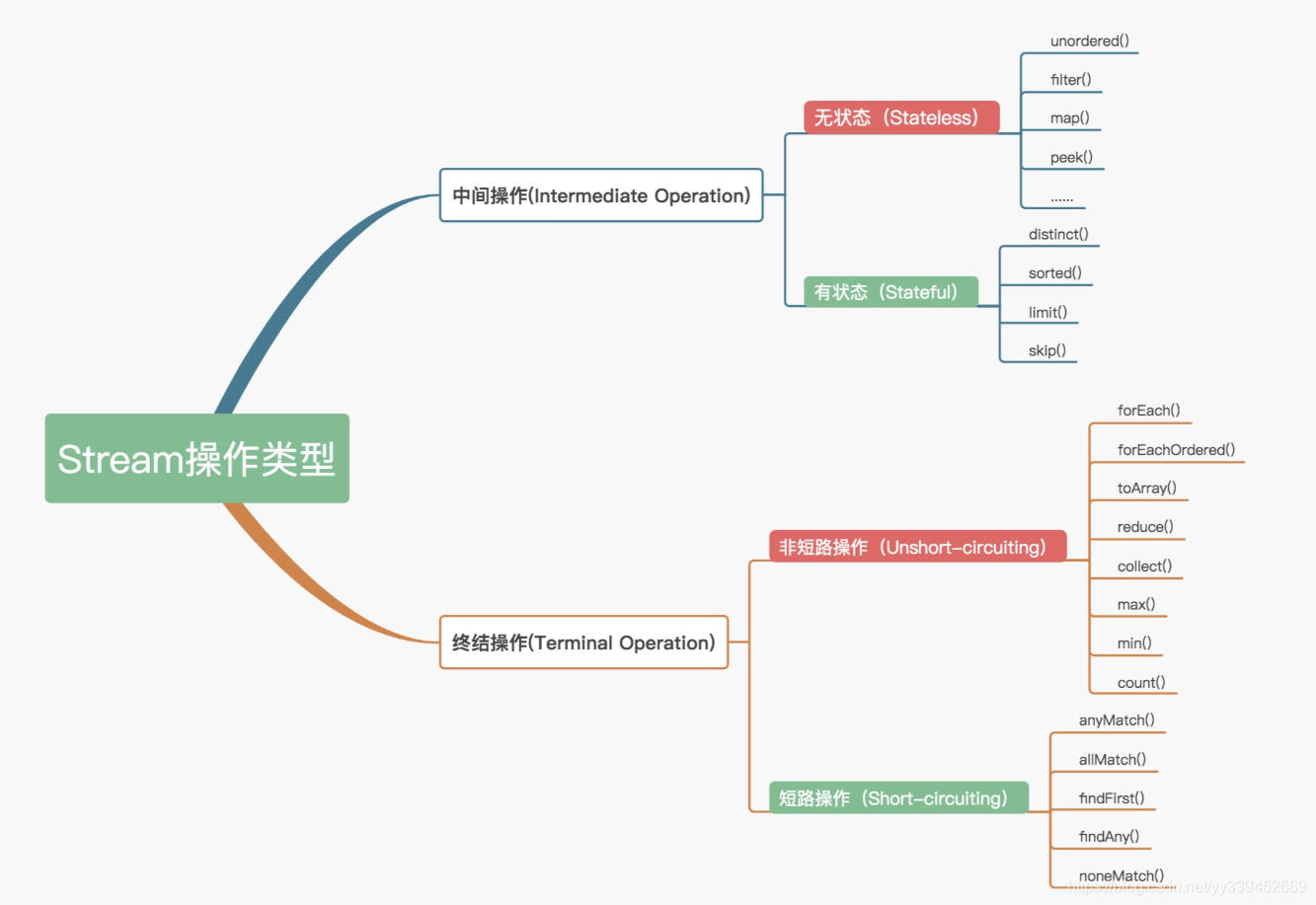
Stream
流创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello","world","stream");
//创建顺序流
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
//创建并行流
Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
|
静态方法
of()、iterate()、generate()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("I", "love", "you", "too");
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, i -> i + 2).limit(3);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream<Boolean> stream3 = Stream.generate(new Random()::nextBoolean).limit(3);
stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
|
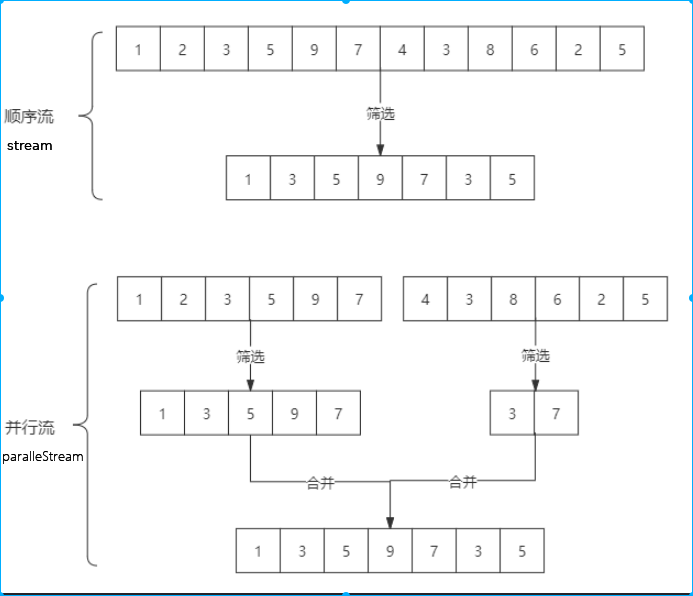
并行流 多线程 把一个内容分成多个数据块 不同线程分别处理每个数据块的流,最后合并(无序数据处理)
1
| Optional<Integer> findFirst = list.stream().parallel().filter( x -> x>4 ).findFirst();
|
可以通过parallel()把顺序流转换成并行流
中间操作
无状态(Stateless)
指元素的处理不受之前元素的影响
filter
筛选,是按照一定的规则校验流中的元素,将符合条件的元素提取到新的流中的操作
1
| list.stream().filter(str->str.length()>3).forEach(System.out::println);
|
相当于if
映射(map、flatMap、peek)
map
1
2
3
4
| List<String> out = list.stream().
map(String::toUpperCase).
collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(out);//[I, LOVE, YOU, TOO]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| List<Product> list = new ArrayList<>();
Test t = new Test();
list.add(t.new Product(1, "domestic phone", new BigDecimal(6899.99)));
list.add(t.new Product(2, "overseas notebook", new BigDecimal(14989.98)));
String out = list.stream().
//map(a->a.name.split(" ")[1]).//phone&¬ebook
map(a->a.name.replaceAll(" ", "-")).//domestic-phone&&overseas-notebook
collect(Collectors.joining("&&"));
System.out.println(out);
|
flatMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a:b:c", "1:3:5");
List<String> listNew = list.stream().
flatMap(s -> Arrays.stream(s.split(":")) ).
collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("处理前的集合:" + list);
System.out.println("处理后的集合:" + listNew);
|
处理前的集合:[a:b:c, 1:3:5]
处理后的集合:[a, b, c, 1, 3, 5]
peek
1
2
| Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("hello", "world");
stream.peek(System.out::println).collect(Collectors.toList());
|
终端操作。通常分为 最终的消费 (foreach 之类的)和 归纳 (collect)两类。
有状态(Stateful)
指该操作只有拿到所有元素之后才能继续下去
distinct
使用hashCode()和equals()方法来获取不同的元素
1
2
3
| Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("1", "3","4","10","4","6","23","3");
stream.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
|
sorted
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1,"phone");
map.put(2,"notebook");
map.entrySet().stream().sorted(
Collections.reverseOrder(Map.Entry.comparingByKey())//倒序
//Comparator.comparing(e -> e.getKey())//正序
).forEach(System.out::println);
|
skip
1
2
| Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(3,1,10,16,8,4,9);
stream.limit(3).skip(2).forEach(System.out::print);
|
limit(3) Iloveyou
skip(2) you
终结操作
短路(Short-circuiting)
指遇到某些符合条件的元素就可以得到最终结果
anyMatch
Stream 中只要有一个元素符合传入的 predicate,返回 true
1
| stream.anyMatch(s->s==2)
|
allMatch
Stream 中全部元素符合传入的 predicate,返回 true
noneMatch
Stream 中没有一个元素符合传入的 predicate,返回 true
findFirst
用于返回满足条件的第一个元素
1
2
3
4
5
| ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("I", "love", "you", "too"));
System.out.println(
list.stream().filter(s-> s.length()>2).findFirst().get()
);
|
findAny
返回流中的任意元素
1
2
3
| System.out.println(
list.parallelStream().filter(s-> s.length()>2).findAny().get()
);
|
love 或 you
并行数据多返回满足第一个
非短路(Unshort-circuiting)
指必须处理完所有元素才能得到最终结果
reduce
reduce操作效率不高,因为它创建了大量的中间String和StringBuilder
1
2
3
| list.stream().
map(a->a.name.replaceAll(" ", "-")).
reduce((str1, str2) -> str1 + "&&" + str2).get();
|
等价 collect(Collectors.joining(“&&”))
toArray
1
2
3
| Product[] array = list.stream().toArray(Product[]::new);
//Arrays.stream(array).sorted(Comparator.comparing(s>s.getId())).forEach(System.out::println);
Arrays.stream(array).filter(s->s.id>1).forEach(System.out::println);
|


